HIGH AVAILABILITY SEAMLESS REDUNDANCY
Fully Rugged Ethernet Switch & Router Solution Features High-Availability Seamless Redundancy (HSR)
MIL CM/CR-6200 Series

OnTime Networks introduced with the CM/CR-6224F4-MIL family the first fully rugged Ethernet switch and router solution which has High-availability Seamless Redundancy (HSR) capabilities for Aerospace and Defense applications. HSR is a new network protocol for Ethernet that provides seamless failover against the failure of a network component. HSR supports dual-port full duplex Ethernet communication and when coupled with IEEE 1588 Precision Time Protocol (PTP) allows for high-accuracy time synchronization between network devices.
Safety and redundancy concepts are common approaches for Aerospace and Defense applications, to ensure that possible system failures have minimal or no impact. As Ethernet systems start to further move into aviation and military systems and sub-systems, such as avionics, weapon stations, display systems, and mission systems, driven by the ease of interconnection, backwards compatibility, and reduced-price points, we also see the demand for newer Ethernet technology concepts and technologies, such as HSR.
What is HSR?
HSR is a new network protocol for Ethernet that provides seamless failover against failure of a network component. HSR supports dual-port full duplex Ethernet communication. When coupled with IEEE 1588 Precision Time Protocol (PTP), HSR allows also for high-accuracy time synchronization between network devices. HSP is suited for applications that require high availability and no switchover time, where the recovery time of commonly used protocols such as the Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) is too long.
HSR provides hardware support (FPGA) to forward or discard frames within microseconds.
Click below for in-depth information regarding High-Availability Seamless Redundancy (HSR).
HSR documentation![]() HSR is suited for applications that request high availability and no switchover time, where the recovery time of commonly used protocols such as the Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) is too long. OnTime Networks’ switches with HSR support provide hardware support (FPGA) to forward or discard frames within microseconds. HSR network nodes, so called DAN H (double attached node for HSR), have at least two gigabit Ethernet ports, each attached to a neighboring HSR node, so that always two paths exist between two HSR nodes. Every HSR node is a switching node, ie. it can forward a frame received on one port to at least one other port in cut-through mode. Therefore, as long as one path is operational, the destination application always receives one frame. HSR nodes check the redundancy continuously to detect lurking failures. The duplicate transmission of frames in both directions comes with a drawback, as effectively only 50% of the network bandwidth is available for data traffic.
HSR is suited for applications that request high availability and no switchover time, where the recovery time of commonly used protocols such as the Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) is too long. OnTime Networks’ switches with HSR support provide hardware support (FPGA) to forward or discard frames within microseconds. HSR network nodes, so called DAN H (double attached node for HSR), have at least two gigabit Ethernet ports, each attached to a neighboring HSR node, so that always two paths exist between two HSR nodes. Every HSR node is a switching node, ie. it can forward a frame received on one port to at least one other port in cut-through mode. Therefore, as long as one path is operational, the destination application always receives one frame. HSR nodes check the redundancy continuously to detect lurking failures. The duplicate transmission of frames in both directions comes with a drawback, as effectively only 50% of the network bandwidth is available for data traffic.

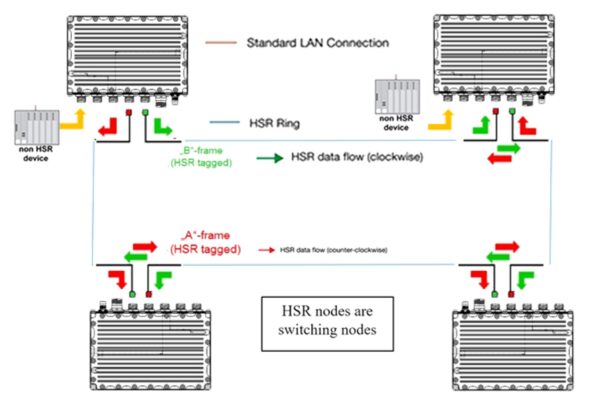
The HSR header is used to encapsulate the Ethernet frame. This has the advantage that duplicates of all frames are recognized in all devices as soon as the HSR header has been received. There is no need to wait for the whole frame to be received before a duplicate can be recognized as such. This means that, similarly to cut-through switching, individual HSR connections and Red Boxes can begin forwarding the frame to the second ring-port as soon as its HSR header has been completely received and duplicate recognition carried out. Each HSR node takes from the network all frames that are addressed only to it and forwards them to the application. Multicast and broadcast messages are forwarded by every node in the ring and are also passed to the application. In order to prevent multicast and broadcast frames from circulating forever, the node that initially placed the multicast or broadcast frame on the ring will remove it as soon as it has completed one cycle.
